Mastering Professional Self-Care for Leadership Success
Introduction

Mastering Professional Self-Care for Leadership Success is a comprehensive session designed to address the critical aspect of professional self-care in leadership. In the demanding world of management, where responsibilities and expectations run high, this exercise emphasizes the importance of setting boundaries, avoiding overcommitment, and honing skills in delegation and time management to maintain a healthy work-life balance. This is a crucial toolkit for mindful leaders aiming to safeguard their well-being, reduce stress, and achieve a harmonious balance that benefits not only themselves but their teams and the entire organization.
Mastering Professional Self-Care for Leadership Success
Listen Now - 3 min. 50 sec.
In this session, we will delve into the crucial aspect of professional self-care. As a mindful leader, you are often faced with demanding responsibilities and expectations. It’s essential to prioritize your well-being by setting boundaries, avoiding overcommitment, and mastering delegation and time management for a healthy work-life balance.
1. Setting Boundaries and Avoiding Overcommitment:
The Importance of Boundaries:
- Setting boundaries is a fundamental aspect of professional self-care. Here are some key points to consider:
– Clarify Your Limits: Define your professional boundaries. Understand what you can and cannot commit to realistically.
– Saying “No” When Necessary: Don’t be afraid to decline additional tasks or commitments when your plate is already full. Saying “no” can be a powerful act of self-care.
Learn more about setting boundaries here.
- Avoiding Overcommitment:
Overcommitment can lead to burnout and stress. Here are strategies to avoid it:
– Prioritize Tasks: Identify your most important tasks and focus on them. Avoid spreading yourself too thin across numerous responsibilities.
– Time Management: Use effective time management techniques to allocate your resources efficiently. Learn to distinguish between urgent and important tasks.
Learn more about overcommitment here.
2. Delegation and Time Management for Work-Life Balance:
- The Art of Delegation:
Delegation is a critical skill for managers. It not only lightens your workload but also empowers your team members. Here’s how to master delegation:
– Identify Tasks: Recognize which tasks can be delegated to team members based on their skills and capabilities.
– Clear Communication: Communicate your expectations clearly when assigning tasks. Provide necessary guidance and resources.
Learn more about delegation here.
- Time Management for Work-Life Balance:
Balancing work and personal life is essential for your well-being. Here are time management tips:
– Prioritize Self-Care: Schedule self-care activities into your daily and weekly routine. Treat them as non-negotiable appointments.
– Efficiency Techniques: Explore time management techniques like the Pomodoro Technique, Eisenhower Matrix, or time blocking to enhance productivity.
Learn more about time management here.
Learn about maintaining a balanced workload here.
Learn about prioritizing tasks for effective leadership here.
Learn about high-pressure decision-making here.
Learn about prioritization and resource allocation here.
Conclusion
We’ve highlighted the significance of professional self-care in your role as a mindful leader. Setting boundaries, avoiding overcommitment, mastering delegation, and effective time management are essential skills that contribute to your well-being and work-life balance.
By implementing these strategies, you can better manage your workload, reduce stress, and maintain a healthier work-life harmony. Remember that taking care of yourself professionally not only benefits you but also positively impacts your team and the overall success of your business.
Setting Boundaries: The Essential Practice for Mindful Leaders
Listen Now - 3 min. 49 sec.
In the fast-paced world of leadership, where demands and responsibilities often blur the lines between personal and professional life, setting boundaries emerges as an essential practice for mindful leaders. The art of boundary-setting is not just about saying no; it’s about affirming your values, managing your energy, and prioritizing your well-being, all of which are crucial for sustainable leadership.
Understanding the Importance of Boundaries
Boundaries are the psychological and emotional limits we set to protect ourselves. For mindful leaders, this means defining what is acceptable and unacceptable in their professional interactions and workload. Establishing clear boundaries helps prevent burnout, reduces stress, and fosters a healthy work environment, leading to more effective leadership and better team dynamics.
The Challenge of Setting Boundaries in Leadership
Many leaders struggle with setting boundaries due to fear of appearing unapproachable or uncommitted. However, the inability to set effective boundaries can lead to overcommitment, exhaustion, and even resentment – factors that are detrimental to both personal health and professional performance.
Steps to Set Effective Boundaries
- Self-Reflection: Begin by understanding your limits. What are your non-negotiables? Recognize the signs of stress and burnout in yourself.
- Clear Communication: Articulate your boundaries clearly to your team and peers. This could involve setting specific work hours, limiting after-hours communication, or delegating tasks.
- Consistency: Enforce your boundaries consistently. Inconsistency can lead to confusion and mismanagement of expectations.
- Lead by Example: As a leader, your actions set a precedent. Respecting your own boundaries encourages your team to do the same.
- Flexibility: While consistency is key, also be flexible. Some situations may require you to adapt your boundaries, but this should be the exception, not the norm.
The Benefits of Setting Boundaries
– Enhanced Focus and Productivity: By limiting distractions and overcommitment, you can focus more effectively on the tasks that matter.
– Improved Work-Life Balance: Boundaries help in distinguishing work from personal life, leading to better relaxation and rejuvenation.
– Empowered Team Members: Clear boundaries can empower your team to take initiative and make decisions within their scope, fostering a sense of trust and responsibility.
Overcoming the Guilt of Setting Boundaries
One common hurdle in setting boundaries is the guilt associated with saying no or delegating tasks. It’s important to realize that setting boundaries is not a sign of weakness; it’s a strategic move for long-term productivity and personal well-being. Remember, a well-rested, focused leader is far more effective than an overworked, stressed one.
Conclusion
In conclusion, setting boundaries is a critical skill for mindful leaders. It requires self-awareness, clear communication, and the courage to prioritize one’s well-being. By mastering this skill, leaders can create a sustainable work environment that not only fosters their own growth but also that of their teams. In the journey of leadership, remember that the first person you need to lead effectively is yourself, and setting boundaries is a pivotal step in that direction.
Understanding Stress: A Mindful Leader’s Guide to Well-being
Listen Now - 3 min. 52 sec.
Introduction
In the dynamic world of leadership, stress is a ubiquitous companion. Mindful leaders recognize that understanding and managing stress is not just a personal endeavor; it’s an essential aspect of effective leadership. In this lesson, we delve into the concept of stress, its root causes, and the profound effects it has on the well-being of mindful leaders.
Understanding Stress
Stress is the body’s natural response to a perceived threat or challenge. This response, often called the “fight-or-flight” reaction, triggers a cascade of physiological and psychological changes designed to prepare us to confront or flee from danger. In moderation, stress can be a motivator, but when chronic or overwhelming, it can have detrimental effects on our physical and mental health.
Causes of Stress
- Work-Related Stress: The demands and pressures of leadership roles, deadlines, high expectations, and constant decision-making contribute to work-related stress.
- Personal Life Challenges: Balancing personal and professional responsibilities, family dynamics, and major life events can also trigger stress.
- Uncertainty and Change: The ever-changing business landscape and unexpected events like crises or disruptions can be significant stressors.
- Perfectionism and High Standards: Mindful leaders often set high standards for themselves and their teams, leading to self-imposed stress.
- Lack of Control: Feeling powerless or unable to influence outcomes can be a significant source of stress.
Effects on Well-being
The effects of stress on mindful leaders are far-reaching and can impact various aspects of their lives:
- Physical Health: Chronic stress can lead to health issues such as high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, weakened immune function, and sleep disturbances.
- Mental Health: Stress is closely linked to mental health concerns like anxiety, depression, and burnout, which can impair leadership effectiveness.
- Decision-Making: High stress can cloud judgment, impede problem-solving abilities, and lead to impulsive decisions.
- Interpersonal Relationships: Stress can strain relationships both at work and in personal life, affecting communication and collaboration.
- Work Performance: Excessive stress can result in reduced productivity, decreased focus, and a diminished capacity for innovation.
Managing Stress Mindfully
Mindful leaders are proactive in managing stress and well-being:
- Self-Care: Prioritize self-care through practices like meditation, exercise, nutrition, and quality sleep.
- Emotional Intelligence: Develop emotional awareness and regulation to manage stress and foster resilience.
- Effective Decision-Making: Enhance decision-making skills and stress-reduction techniques.
- Team Resilience: Foster a culture of resilience within your team through open communication and support.
- Continuous Learning: Invest in learning and adapting to better handle stress and uncertainties.
Conclusion
Stress is an inherent part of leadership, but it doesn’t have to be an insurmountable burden. Mindful leaders recognize that by understanding the causes and effects of stress and proactively managing it, they can not only safeguard their well-being but also lead with clarity, compassion, and effectiveness. In the ever-evolving landscape of mindful leadership, stress management is a cornerstone of enduring success and well-being.
Recognizing the Signs: A Mindful Leader’s Guide to Identifying Stress
Listen Now - 3 min. 36 sec.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of leadership, stress can become a constant companion. Mindful leaders understand that recognizing the signs and symptoms of stress is not just essential for their well-being but also for their leadership effectiveness. In this lesson, we will explore common indicators of stress and provide guidance on how to recognize them.
Physical Signs of Stress
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness, even after a full night’s sleep, can be a sign of stress-induced exhaustion.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches, especially tension headaches, can be a physical manifestation of stress.
- Muscle Tension: Stress often leads to muscle tension, resulting in stiffness or discomfort.
- Digestive Issues: Upset stomach, indigestion, and changes in appetite can be stress-related.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restless sleep are common stress-related sleep problems.
Emotional Signs of Stress
- Irritability: Becoming easily irritated, short-tempered, or snapping at others can indicate heightened stress levels.
- Anxiety: Excessive worry, restlessness, and feelings of unease are typical emotional responses to stress.
- Depression: Prolonged stress can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities.
- Mood Swings: Stress can cause mood fluctuations, from elation to irritability and back.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Reduced focus, forgetfulness, and indecisiveness are cognitive symptoms of stress.
Behavioral Signs of Stress
- Increased Aggression: Stress may lead to an increase in aggressive or impulsive behaviors.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoiding social interactions or withdrawing from relationships can be a response to stress.
- Procrastination: Putting off tasks or neglecting responsibilities may occur due to stress-related overwhelm.
- Changes in Habits: Stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating, excessive alcohol consumption, or smoking.
Recognizing Stress in Yourself
To identify stress in yourself as a mindful leader, pay attention to these signs:
- Monitor Your Body: Notice any physical discomfort or changes in your body.
- Emotional Check-in: Reflect on your emotions and assess if they align with your usual state.
- Behavioral Patterns: Be aware of any sudden shifts in your behavior or habits.
- Self-Reflection: Regularly take time to self-reflect and evaluate your stress levels.
Recognizing Stress in Others
As a mindful leader, recognizing stress in your team members is equally important. Watch for changes in their behavior, productivity, and mood. Offer support and encourage open communication to help them cope with stress effectively.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of stress is the first step toward effective stress management. Mindful leaders prioritize self-awareness and the well-being of their teams. By identifying stress early and implementing stress-reduction strategies, leaders can maintain their own well-being and create a supportive, resilient environment for their organizations.
Time Management Techniques for Leaders: Staying Organized and Focused
Listen Now - 7 min. 7 sec.
In the world of leadership, time is a precious resource. Effective time management isn’t just about getting more done; it’s about making the most of your time to achieve your goals while maintaining focus, reducing stress, and fostering a sense of balance. Here are some time management techniques to help leaders stay organized and focused:
- Prioritize with Purpose:
Successful leaders understand that not all tasks are created equal. The Eisenhower Matrix (see below), which categorizes tasks into four quadrants (urgent and important, important but not urgent, urgent but not important, neither urgent nor important), is a powerful tool for prioritization. Focus on the tasks in the “urgent and important” quadrant while delegating or scheduling tasks in the other quadrants.
- Set SMART Goals:
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals provide a clear roadmap for your work. Leaders should define SMART goals to ensure they stay on track and maintain focus on what truly matters.
- Time Blocking:
Allocate specific time blocks for different types of tasks. For example, designate a block for meetings, another for focused work, and another for email and communication. This method minimizes multitasking and helps you concentrate on one task at a time.
- Eliminate Time Wasters:
Identify common time-wasting activities and minimize or eliminate them. This might include reducing excessive meetings, limiting distractions from social media, or setting boundaries on interruptions.
- Delegate Effectively:
Leaders should delegate tasks that can be handled by others, allowing them to focus on strategic and high-impact activities. Effective delegation empowers team members and lightens the leader’s workload.
- Use Technology Wisely:
Leverage productivity tools and apps to streamline tasks and stay organized. Calendar apps, project management software, and task management apps can help leaders track deadlines and responsibilities efficiently.
- Practice the Two-Minute Rule:
If a task can be completed in two minutes or less, do it immediately. This rule reduces the accumulation of small tasks that can clutter your to-do list.
- Batch Similar Tasks:
Group similar tasks together and tackle them in one go. This approach minimizes context-switching and enhances focus. For example, dedicate a specific time each day to respond to emails or make phone calls.
- Take Regular Breaks:
Scheduled breaks are essential for maintaining focus and productivity. Short breaks, such as the Pomodoro Technique (25 minutes of work followed by a 5-minute break), can re-energize you for the next task.
- Learn to Say No:
Leaders often face an abundance of opportunities and requests. Politely declining commitments that don’t align with your goals and priorities is crucial to protect your time and maintain focus on what truly matters.
- Reflect and Adjust:
Regularly assess your time management strategies. What’s working? What isn’t? Be open to adjustments and improvements in your approach.
- Invest in Self-Care:
Leaders who prioritize self-care, including exercise, adequate sleep, and mindfulness practices, are better equipped to manage their time effectively. A healthy body and mind are essential for sustained productivity.
Conclusion:
Effective time management is a cornerstone of successful leadership. By implementing these time management techniques, leaders can optimize their use of time, stay organized, and maintain the focus needed to achieve their goals while leading their teams to success. It’s a journey of continuous improvement, and as leaders master the art of time management, they empower themselves to lead with clarity, purpose, and balance.
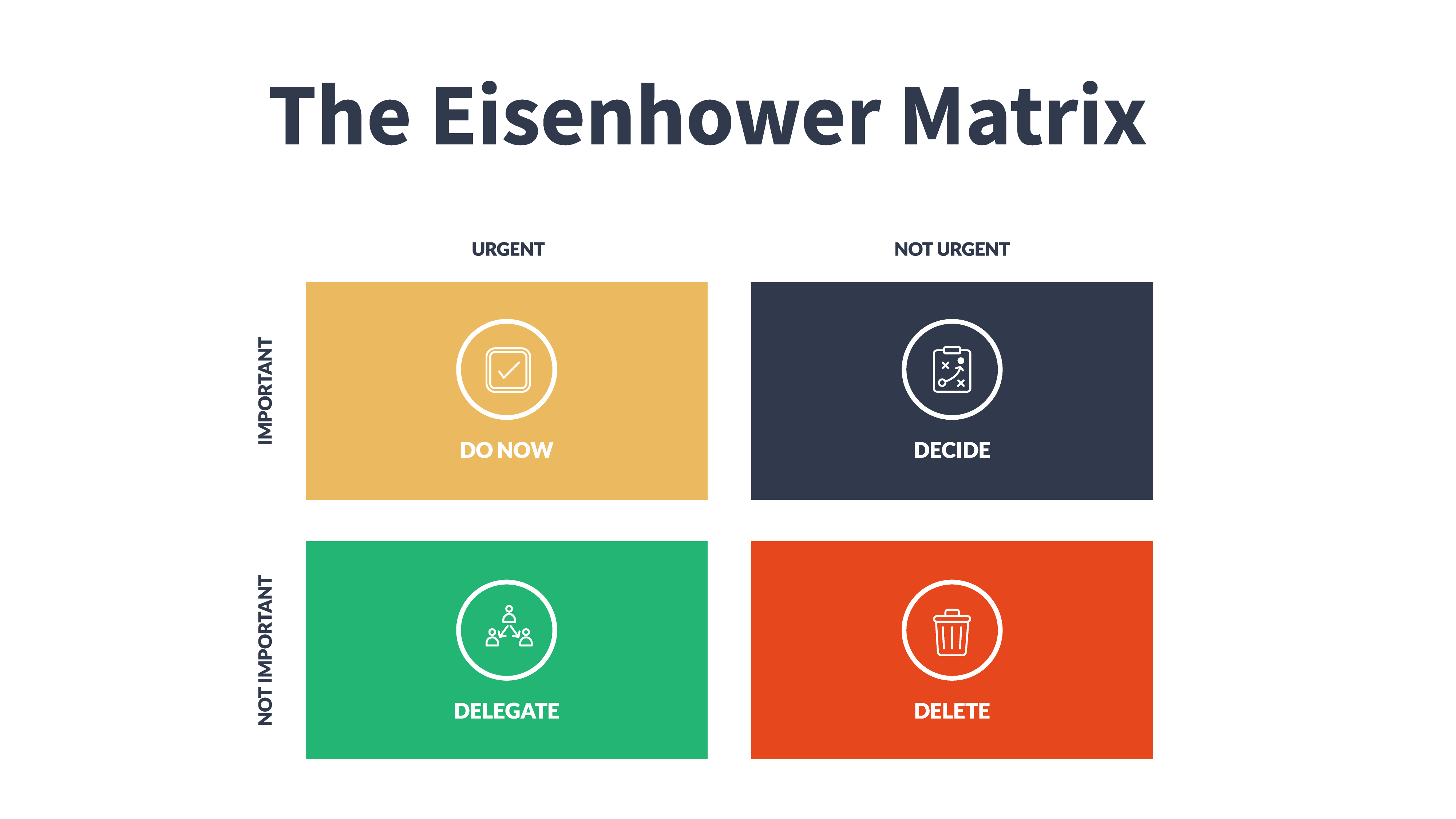
The Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Eisenhower Box or Urgent-Important Matrix, is a simple yet powerful tool for prioritizing tasks and managing time effectively. It was popularized by the 34th President of the United States, Dwight D. Eisenhower, who was known for his exceptional time management skills.
The matrix divides tasks into four categories based on two key criteria: urgency and importance. Here’s how it works:
- Quadrant 1 – Urgent and Important: Tasks in this quadrant are both urgent and important. They require immediate attention and should be your top priority. These tasks often involve critical deadlines, emergencies, or issues that demand your immediate focus and action.
- Quadrant 2 – Not Urgent but Important: Tasks in this quadrant are important but not immediately urgent. They contribute to your long-term goals, personal growth, and strategic objectives. Effective leaders spend a significant amount of their time in this quadrant, as it’s where proactive planning, skill development, and relationship-building occur.
- Quadrant 3 – Urgent but Not Important: Tasks in this quadrant are urgent but lack significant long-term importance. They often involve interruptions, distractions, or requests from others that may not align with your priorities. While they may need to be addressed, it’s essential to minimize time spent on these tasks to maintain focus on what truly matters.
- Quadrant 4 – Neither Urgent nor Important: Tasks in this quadrant are neither urgent nor important. They are often time-wasters and distractions that can be safely eliminated or delegated. Leaders should aim to reduce or eliminate these tasks to free up valuable time.
The Eisenhower Matrix is a visual tool that allows individuals to assess their tasks and allocate them to the appropriate quadrant. By doing so, it helps leaders make informed decisions about how to prioritize their work, minimize procrastination, and maintain a clear focus on activities that align with their goals and values. It’s a valuable technique for enhancing productivity, time management, and overall effectiveness in both personal and professional life.
Delegation and Effective Communication for Leaders
Listen Now - 4 min. 4 sec.
Introduction:
Delegation is a crucial skill for leaders. It not only lightens your workload but also empowers your team members to grow and take ownership of their work. However, successful delegation requires careful consideration of which tasks to delegate and clear communication of expectations. In this lesson, we will explore the art of identifying tasks suitable for delegation and how to communicate effectively with your team.
Part 1: Identifying Tasks for Delegation
- Assess Your Strengths and Weaknesses:
– Identify tasks that align with your strengths and those that may not be your forte. Delegate tasks that are outside your expertise.
- Evaluate Task Complexity:
– Determine the complexity of each task. Delegate routine, well-defined tasks that can be easily explained and executed.
- Identify Repetitive or Time-Consuming Tasks:
– Look for tasks that are repetitive or time-consuming but don’t necessarily require your unique skills. These are prime candidates for delegation.
- Consider Team Members’ Skills:
– Know your team’s strengths and weaknesses. Match tasks with team members who have the right skills and expertise to handle them effectively.
- Evaluate Urgency and Priority:
– Delegate tasks based on their urgency and priority. Ensure that you have the bandwidth to oversee critical tasks while delegating less urgent ones.
Part 2: Effective Communication of Expectations
- Define Clear Objectives:
– Clearly articulate the objectives and desired outcomes of the delegated task. Ensure that your team member understands the purpose and end goals.
- Specify Scope and Boundaries:
– Set boundaries and limitations for the task, including what is within and outside the scope of the assignment.
- Provide Resources and Support:
– Offer the necessary resources, tools, and support to help your team member complete the task successfully.
- Establish a Timeline:
– Set a realistic deadline for task completion. Ensure that it aligns with other priorities and allows sufficient time for quality work.
- Encourage Questions and Clarifications:
– Create an open environment where team members feel comfortable asking questions and seeking clarifications about the task.
- Foster Accountability:
– Clearly communicate that the team member is responsible for the task’s success and outcomes. Encourage accountability.
- Maintain Open Communication:
– Stay accessible for updates, progress reports, and feedback. Regular check-ins can prevent misunderstandings and ensure alignment.
- Provide Feedback and Recognition:
– Offer constructive feedback on completed tasks and recognize team members for their efforts and achievements.
- Trust and Empower:
– Trust your team members to handle delegated tasks independently. Empower them to make decisions within the defined scope.
- Learn from Feedback:
– Use feedback from delegated tasks to refine your delegation skills. Continuous improvement is key to effective delegation.
Effective delegation and communication of expectations are essential leadership skills. By identifying suitable tasks for delegation and mastering clear and open communication, you empower your team, foster growth, and free up your own time to focus on strategic leadership. Remember that delegation is not just about assigning tasks but also about building trust and collaboration within your team.
Benefits of Delegation for Leaders:
- Time Management: Delegation allows leaders to prioritize their time and focus on strategic tasks and high-impact activities.
- Increased Productivity: Leaders can accomplish more by sharing the workload, leading to increased overall productivity.
- Skill Development: Delegation provides opportunities for team members to develop new skills and take on more responsibilities, enhancing their capabilities.
- Empowerment: Empowered team members take ownership of their work, leading to higher job satisfaction and motivation.
- Effective Task Management: Leaders can ensure that tasks align with the right skills and expertise, leading to better task execution.
- Strategic Focus: Delegation frees leaders to concentrate on long-term goals and strategic planning.
- Leadership Growth: Delegating tasks fosters leadership growth by enabling leaders to focus on their core leadership responsibilities.
- Work-Life Balance: Effective delegation contributes to a better work-life balance for leaders, reducing burnout and stress.
Benefits of Delegation for Team Members:
- Skill Enhancement: Team members have opportunities to develop new skills and gain valuable experience through delegated tasks.
- Increased Motivation: Being entrusted with tasks motivates team members, boosting their engagement and commitment.
- Career Growth: Successful delegation can lead to career advancement as team members demonstrate their capabilities.
- Ownership and Responsibility: Delegated tasks provide a sense of ownership and responsibility, making team members feel more invested in their work.
- Learning Opportunities: Delegation offers learning opportunities as team members tackle new challenges and problem-solving.
- Professional Development: Team members can enhance their professional development by taking on tasks that expand their knowledge and abilities.
- Recognition: Successful completion of delegated tasks often results in recognition and acknowledgment, boosting team members’ morale.
- Collaboration: Delegation encourages collaboration and a sense of unity within the team as members work together to achieve common goals.
- Time Management Skills: Team members learn to manage their time effectively and prioritize tasks when they take on delegated responsibilities.
In summary, delegation benefits both leaders and team members by optimizing productivity, fostering skill development, enhancing motivation, and promoting professional growth. It is a valuable practice that contributes to the overall success and well-being of a team and organization.
Practical Tips for Leaders to Maintain a Balanced Workload
Listen Now - 3 min. 49 sec.
- Set Clear Priorities: Identify your most important tasks and align them with your leadership goals. Focus on what truly matters and allocate your time accordingly.
- Delegate Effectively: Trust your team members and delegate tasks to them based on their strengths and expertise. This not only lightens your load but also empowers your team to grow.
- Use Time Management Tools: Employ time management tools and techniques such as calendars, to-do lists, and task management apps to stay organized and on track.
- Time Blocking: Allocate specific time blocks for different types of tasks. Create dedicated time for important but not urgent tasks to prevent them from becoming crises.
- Set Boundaries: Establish clear boundaries for work hours and non-work time. Avoid the temptation to overwork, and prioritize self-care and personal life.
- Learn to Say No: Don’t overcommit. Politely decline tasks or commitments that don’t align with your priorities or would overload your schedule.
- Batch Similar Tasks: Group similar tasks together and tackle them during designated time blocks. This minimizes context switching and enhances efficiency.
- Avoid Multitasking: Focus on one task at a time. Multitasking can reduce productivity and quality of work.
- Regular Breaks: Take short breaks throughout the day to recharge. Even a few minutes of stretching or deep breathing can refresh your mind.
- Block Off Thinking Time: Schedule time for reflection and strategic thinking. This allows you to plan and make decisions more effectively.
- Set Realistic Goals: Avoid setting unrealistic expectations for yourself or your team. Realistic goals prevent burnout and promote work-life balance.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: Periodically review your workload and commitments. Adjust your priorities and delegate as needed to maintain balance.
- Seek Support and Feedback: Discuss workload concerns with mentors, colleagues, or coaches. They can provide valuable insights and advice.
- Self-Care: Prioritize self-care practices, including exercise, meditation, and spending time with loved ones. A well-rested and healthy leader is more effective.
- Continuous Learning: Invest in personal and professional development to improve your leadership skills. Learning can lead to more efficient decision-making and problem-solving.
- Model Balance: Lead by example and encourage a balanced workload culture within your team or organization. Show that work-life balance is important.
- Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate accomplishments, both big and small. This boosts morale and motivates you to maintain balance.
- Evaluate and Adjust: Regularly assess your workload and make adjustments as needed. Adapt to changing circumstances and challenges.
Balancing a leadership workload is essential for sustainable success and well-being. Implementing these practical tips can help leaders maintain equilibrium, make informed decisions, and lead with clarity and effectiveness.
Prioritizing Tasks for Effective Leadership
Listen Now - 3 min. 41 sec.
Effective leadership often involves juggling multiple tasks and responsibilities. To make the most of your time and energy, it’s crucial to identify and prioritize tasks based on their importance and urgency. This lesson will provide you with a framework for better task management and decision-making, allowing you to lead more efficiently and purposefully.
Step 1: The Eisenhower Matrix (Quadrant Method)
One of the most effective tools for task prioritization is the Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Quadrant Method. This method categorizes tasks into four quadrants based on their importance and urgency:
Quadrant 1: Urgent and Important (Do First)
Tasks in this quadrant require immediate attention. They are both important to your leadership role and time-sensitive. Focus on these tasks first to prevent crises and maintain control.
Quadrant 2: Important but Not Urgent (Schedule)
These tasks are vital for long-term success but don’t require immediate action. Schedule them for future execution. Effective leaders invest time in Quadrant 2 to prevent crises from emerging in Quadrant 1.
Quadrant 3: Urgent but Not Important (Delegate)
Tasks here may seem pressing but do not contribute significantly to your leadership goals. Delegate these responsibilities to team members whenever possible to free up your time.
Quadrant 4: Neither Urgent nor Important (Eliminate)
Tasks in this quadrant are time-wasters and distractions. Eliminate or minimize them from your work to focus on what truly matters.
Step 2: Assessing Importance and Impact
In addition to the Eisenhower Matrix, consider assessing tasks based on their long-term importance and impact on your leadership objectives. Some tasks may not be urgent but can significantly advance your goals.
– Identify tasks that align with your strategic leadership objectives and mission.
– Evaluate the potential impact of each task on your team, organization, or personal growth.
– Prioritize tasks that contribute to your long-term vision, even if they aren’t urgent.
Step 3: Time Blocking and Scheduling
Once you’ve categorized and assessed tasks, create a structured schedule. Use time-blocking techniques to allocate specific time slots for different types of tasks. This approach ensures you dedicate focused time to important but not urgent tasks (Quadrant 2).
Step 4: Flexibility and Adaptation
Leaders often face unexpected challenges and opportunities. Remain flexible in your task management approach. Adjust your priorities as needed to address urgent issues, but always keep your long-term objectives in mind.
Prioritizing tasks based on importance and urgency is a fundamental skill for effective leadership. By using tools like the Eisenhower Matrix and considering the long-term impact of your actions, you can lead with purpose, maximize productivity, and drive meaningful results for your team and organization. Remember that effective leadership involves both managing tasks and inspiring and guiding your team toward a shared vision.
Mastering High-Pressure Decision-Making: Strategies for Leaders
Listen Now - 4 min. 38 sec.
In the dynamic world of leadership, high-pressure situations are par for the course. Whether it’s responding to a crisis, making critical business decisions, or navigating a complex problem, leaders must excel at decision-making under pressure. To succeed in these demanding moments, leaders can employ a set of effective strategies that not only lead to sound decisions but also maintain composure and inspire confidence.
- Embrace a Structured Approach:
One of the keys to effective decision-making under pressure is to adopt a structured approach. The following frameworks can help:
– SWOT Analysis: Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with each option.
– Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh the pros and cons of each choice in terms of both short-term and long-term outcomes.
– Decision Trees: Visualize potential decisions and their consequences, helping to make informed choices.
- Gather Information Reliably:
In high-pressure situations, it’s essential to base decisions on accurate and up-to-date information. Leaders should:
– Establish Trusted Sources: Identify reliable sources of information that can be quickly accessed when needed.
– Cross-Check Data: Verify information from multiple sources to reduce the risk of relying on misinformation.
- Prioritize Objectivity:
High-pressure environments can trigger emotional responses that cloud judgment. Leaders should strive for objectivity by:
– Delaying Immediate Reactions: Avoid making snap decisions. Take a moment to breathe and think before acting.
– Soliciting Input: Seek input from team members or trusted advisors to gain different perspectives.
- Establish Clear Criteria:
Set clear criteria for decision-making that align with your organization’s values and goals. This clarity helps leaders focus on what truly matters.
- Consider Contingencies:
Anticipate potential outcomes and have contingency plans in place. Effective leaders consider “what if” scenarios to adapt swiftly when circumstances change.
- Communicate Transparently:
Communication is critical during high-pressure decision-making. Leaders should:
– Share Rationale (aka the “why”): Communicate the reasoning behind your decisions to foster understanding.
– Clarify Expectations: Clearly define roles and responsibilities to ensure everyone knows their part.
- Manage Time Wisely:
In high-pressure situations, time can be a limited resource. Leaders should:
– Set Time Limits: Establish a deadline for decision-making to prevent analysis paralysis.
– Prioritize Urgency: Address the most time-sensitive aspects first, then work on longer-term solutions.
- Reflect and Learn:
After the dust has settled, leaders should review their decisions and outcomes to identify lessons learned. This practice ensures continuous improvement and adaptation for future high-pressure scenarios.
- Seek Mentorship and Training:
Leaders can benefit from mentorship and training programs that focus on decision-making under pressure. Learning from experienced mentors and participating in simulations can enhance these skills.
- Self-Care and Resilience:
Leaders must prioritize self-care to maintain resilience in high-pressure situations. Practices like mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can enhance mental and emotional strength.
Conclusion:
Leadership in high-pressure environments demands a combination of strategy, self-awareness, and adaptability. By embracing structured decision-making approaches, staying objective, and fostering clear communication, leaders can navigate turbulent waters with confidence. Remember that mastering high-pressure decision-making is an ongoing journey, and continuous learning and improvement are key to success in leadership roles.
Prioritization and Resource Allocation for Mindful Leaders
Listen Now - 4 min. 32 sec.
In the ever-evolving landscape of leadership, one of the most critical skills a mindful leader can possess is the ability to prioritize effectively and allocate resources wisely. By mastering this skill, leaders can steer their organizations toward success while maintaining a sense of balance and alignment with their core values. Here’s a closer look at the importance of prioritization and resource allocation for mindful leaders:
The Art of Prioritization:
Prioritization is the process of determining which tasks, projects, or initiatives should take precedence based on their significance and impact. For mindful leaders, this process involves not only assessing the external factors but also aligning decisions with their values and long-term vision. Here are some key aspects of prioritization:
- Clarity of Purpose: Mindful leaders have a clear sense of purpose, both personally and professionally. This purpose serves as a guiding light when evaluating what deserves their attention and resources.
- Alignment with Values: Every decision and priority should align with the leader’s core values. Prioritizing in line with these values ensures that actions are consistent with what truly matters.
- Impact Assessment: Leaders assess the potential impact of their choices. They consider which actions will lead to the most significant positive outcomes for themselves, their teams, and their organizations.
- Balancing Urgency and Importance: Mindful leaders use frameworks like the Eisenhower Matrix to categorize tasks by urgency and importance, helping them distinguish between what’s pressing and what’s truly significant.
Resource Allocation:
Resource allocation involves distributing available resources, such as time, budget, manpower, and energy, to various tasks or projects. For mindful leaders, resource allocation is a strategic process that aligns with their prioritization efforts:
- Effective Time Management: Time is one of the most valuable resources for leaders. Mindful leaders allocate their time in a way that balances daily responsibilities with long-term goals and self-care.
- Budget Allocation: Financial resources are managed carefully, with an emphasis on investing in areas that support the organization’s mission and vision.
- Personnel Deployment: Leaders allocate team members to projects based on their skills, strengths, and the project’s importance. They also consider team members’ workload to prevent burnout.
- Energy and Focus: Mindful leaders recognize the importance of mental and emotional energy. They allocate time for mindfulness practices, exercise, and relaxation to maintain their well-being and resilience.
Challenges and Strategies:
Mindful leaders are not immune to challenges in prioritization and resource allocation. Here are some common obstacles and strategies to overcome them:
– Overcommitment: Mindful leaders avoid overcommitting by learning to say no when necessary and setting realistic expectations for themselves and their teams.
– Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Leaders strike a balance between addressing immediate needs and working toward long-term objectives. They allocate resources accordingly, ensuring the organization’s sustainability.
– Adaptability: Mindful leaders remain adaptable and open to adjustments in their priorities and resource allocation as circumstances change. They embrace continuous learning and flexibility.
Conclusion:
Prioritization and resource allocation are essential skills for mindful leaders who seek to create harmonious and purpose-driven organizations. By aligning choices with core values, assessing impact, and managing resources strategically, leaders can navigate the complexities of leadership with grace and authenticity. In doing so, they inspire their teams and create a culture of mindfulness, purpose, and sustainable success.
Overcoming Overcommitment: A Guide for Mindful Leaders
Listen Now - 4 min. 4 sec.
In the realm of leadership, the temptation to take on more than we can handle is a common pitfall. Overcommitment, the state of engaging in more tasks or responsibilities than one can manage, is a pervasive issue in the world of leadership. It’s a silent productivity killer, often cloaked in the guise of ambition and diligence. For mindful leaders, understanding and avoiding overcommitment is not just a strategy for personal well-being, but a crucial element of effective leadership.
The Perils of Overcommitment
Overcommitment stretches leaders thin, leading to diminished quality of work, increased stress, and potential burnout. It can also erode team morale, as leaders unable to manage their workload effectively may inadvertently neglect their team’s needs or fail to provide adequate support and guidance.
Read more:
“Practical Tips for Leaders to Maintain a Balanced Workload”
“Understanding Stress: A Mindful Leader’s Guide to Well-being”
“Recognizing the Signs: A Mindful Leader’s Guide to Identifying Stress”
Identifying Overcommitment
The first step in avoiding overcommitment is recognizing it. Common signs include a consistently overloaded schedule, a feeling of being constantly behind, and a decrease in the quality of work. If you find yourself routinely working long hours just to keep up, or if your work-life balance has tilted unfavorably towards work, these are clear indicators of overcommitment.
Strategies to Avoid Overcommitment
- Prioritize and Delegate: Understand your key responsibilities and prioritize them. Delegate tasks that can be handled by others. Remember, delegation is not a sign of weakness but a strategic leadership tool.
- Set Realistic Goals and Expectations: Be realistic about what you can achieve in the given time frame. Overly ambitious goals can lead to overcommitment.
- Learn to Say No: Perhaps the most crucial skill in avoiding overcommitment is learning to say no. This means declining additional responsibilities that do not align with your priorities or capacity.
- Time Management: Efficient time management is vital. Use techniques like the Eisenhower Box or Pomodoro Technique to organize and prioritize tasks effectively.
- Regular Self-Review: Periodically review your commitments. Are they aligning with your goals? Do you need to make adjustments?
- Mindfulness and Self-awareness: Practice mindfulness to stay aware of your stress levels and work patterns. This self-awareness can help you recognize the early signs of overcommitment.
Read more:
”Delegation and Effective Communication for Leaders”
“Prioritizing Tasks for Effective Leadership”
“Mastering High-Pressure Decision-Making: Strategies for Mindful Leaders”
“Prioritization and Resource Allocation for Mindful Leaders”
“Time Management Techniques for Leaders: Staying Organized and Focused”
The Power of Mindful Leadership
Mindful leadership is about understanding the impact of your actions on yourself and your team. By avoiding overcommitment, you not only safeguard your well-being but also set a positive example for your team. A leader who manages their commitments well inspires the team to do the same, leading to a more balanced, productive, and harmonious work environment.
Embracing Flexibility and Adaptability
Avoiding overcommitment doesn’t mean being rigid. It requires flexibility and the ability to adapt as situations change. What is important is maintaining a balance and being aware of your limits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, avoiding overcommitment is a crucial aspect of mindful leadership. It involves understanding your limits, setting realistic goals, prioritizing effectively, and being aware of the impact of your workload on your well-being and that of your team. Mindful leaders who manage their commitments effectively not only enjoy a better quality of life but also foster a more positive, productive work environment. Remember, in the journey of leadership, the ability to manage your commitments is as important as the commitments themselves.

CONTACT US
+61 475 866 592